Thermal Mass Flowmeter Principle
What is Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeters?

A thermal mass flow meter is a precision instrument that measures gas mass flow and is used in various industries with a wide range of applications.
Thermal Mass Flowmeter Working Principle
Thermal mass flowmeters operate on an interesting working principle of Hot-wire Anemometers. A core of Anemometer is exposed to constant heat and the heat convected by the fluid passing by the anemometer is noted to measure the fluid velocity. Similarly, instead of using fluid momentum, thermal mass flowmeters make use of the thermal or heat conducting properties of fluids to determine the mass flow.
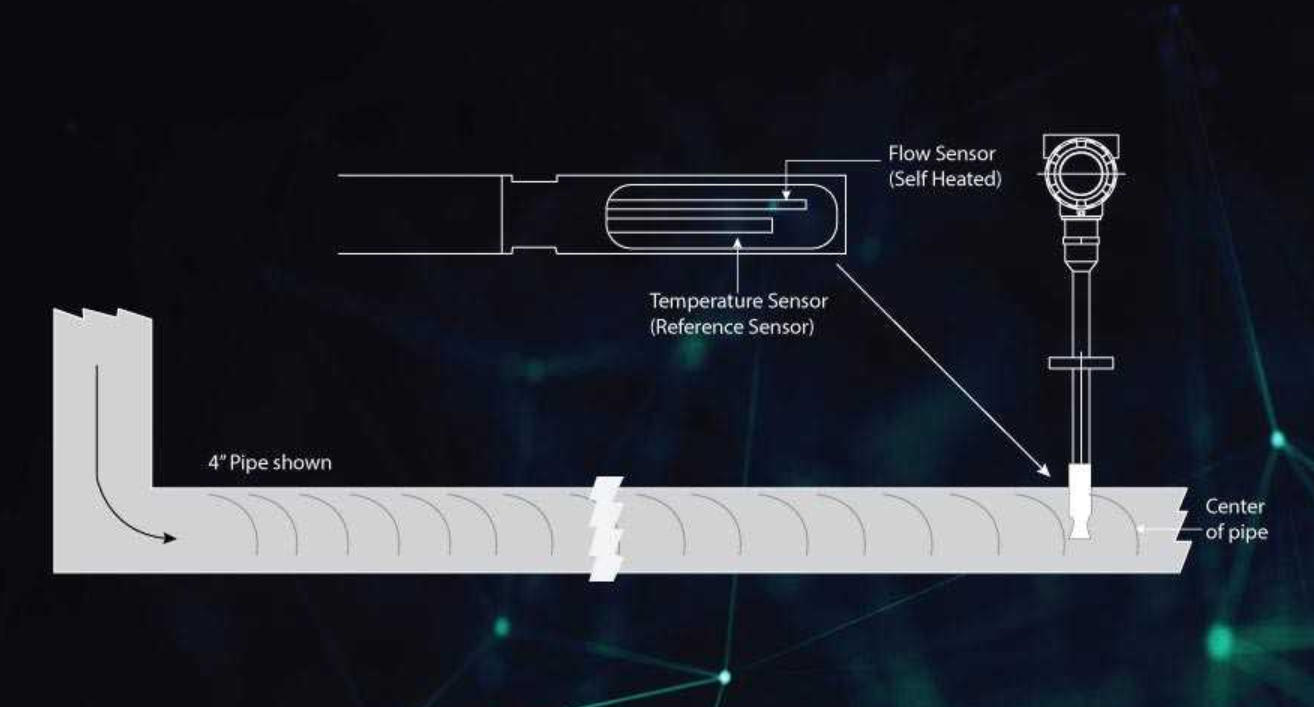
The thermal mass flowmeter is available in high-performance Inline type and Insertion type flowmeters. Insertion flowmeters consist of a probe with sensing elements that are inserted into the pipe irrespective of pipe size. These are easy to install and more economical. Inline flowmeters are connected to the pipe itself by the flanged or threaded connection. Inline meters are suitable for smaller diameter pipes.
The thermal mass flowmeter is comprised of a family of instruments for precision mass flow measurement. The sensor probe is inserted in the center line of the flow. Thermal mass flowmeters use the concept of heat dissipations for mass flow calculations. Two sensors, both resistive temperature detectors (RTDs), are immersed into the stream of flow under measurement. The first sensor, referred to as a velocity sensor, has a heating element in it and it monitors mass flow rate. The second sensor, which is referred to as a temperature sensor, measures the actual temperature of the gas flowing in the pipe as a reference regardless of the flow velocity. Every gas molecule has an ability to absorb heat. Thus when the gas flows through the pipe, heat from the first sensor (velocity sensor) is absorbed by the gas molecules. As these molecules reach the next sensor (temperature sensor) heat is dissipated and is sensed by this sensor instantaneously. The amount of heat absorbed by the gas molecules is directly proportional to the number of molecules passing the velocity sensor which is nothing but the mass flow rate. This can be mathematically expressed as:
To calculate the volumetric flow rate:
m = K (H/ ΔT)1.67
Where,
m = mass flow rate
K = proportionality constant
H = Heat loss
ΔT = Temperature difference
Two methods, Constant Temperature Difference and Constant Power, are used for mass flow measurement and both methods obtain the same results.
Advantages of Mass Flow Measurement
- Thermal flow meters have no moving parts, which reduces maintenance and permits the use in demanding application areas, including saturated gas.
- Gas mass meters calculate mass flow rather than volumetric flow and do not require temperature or pressure correction, which means there is no additional expense for the purchase and installation of additional equipment.
- Thermal flowmeters provide excellent accuracy and repeatability over a wide range of flow rates.
- Thermal flow meters can measure flow in large pipes.

